Karyotyping and diagnosis of diseases
written by Eddy
A karyogram or idiogram is a graphical depiction of a karyotype, wherein chromosomes are generally organized in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size. Karyotyping generally combines light microscopy and photography in the metaphase of the cell cycle, and results in a photomicrographic (or simply micrographic) karyogram.
In karyotype, it is possible to investigate diseases caused by different chromosomes.
For example, Down syndrome is caused by trisomy 21.
In Generative Art: Karyotype, the diseases caused by sex chromosomes have been examined, which will be discuss in detail.
project name project name project name
project name project name project name
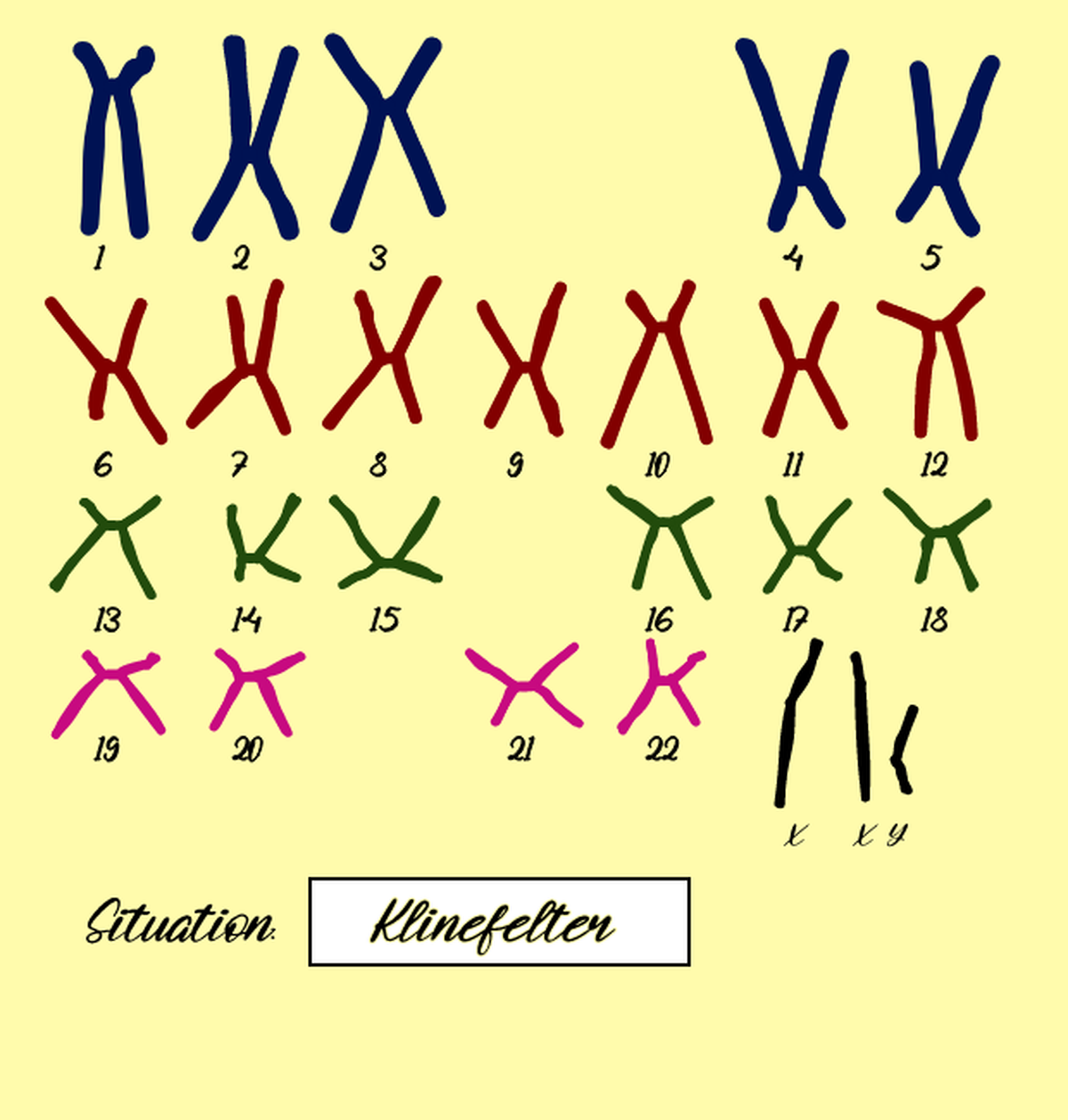
1)Klinefelter-syndrome:
Klinefelter syndrome (sometimes called Klinefelter's, KS or XXY) is where boys and men are born with an extra X chromosome. Chromosomes are packages of genes found in every cell in the body. There are 2 types of chromosome, called the sex chromosomes, that determine the genetic sex of a baby.
Signs and symptoms may include:
Low sperm count or no sperm.
Small testicles and penis.
Low sex drive.
Taller than average height.
Weak bones.
Decreased facial and body hair.
Less muscular compared with other men.
Enlarged breast tissue
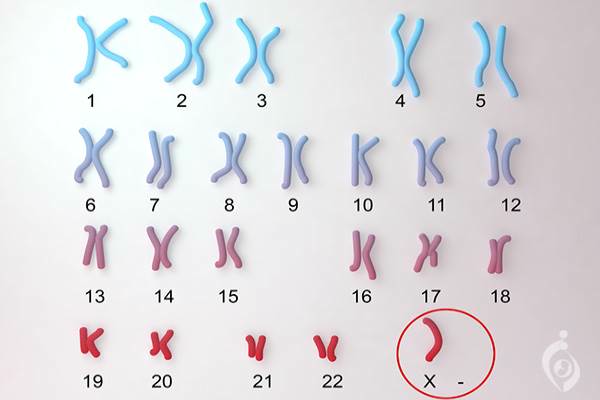
2)Turner syndrome:Turner syndrome, a condition that affects only females, results when one of the X chromosomes (sex chromosomes) is missing or partially missing. Turner syndrome can cause a variety of medical and developmental problems, including short height, failure of the ovaries to develop and heart defects.Karyotyping is a test that involves analysing the 23 pairs of chromosomes. It's often used when Turner syndrome is suspected. The test can either be carried out while the baby is inside the womb – by taking a sample of amniotic fluid (amniocentesis) – or after birth by taking a sample of the baby's blood
Karyotyping is a test that involves analysing the 23 pairs of chromosomes. It's often used when Turner syndrome is suspected. The test can either be carried out while the baby is inside the womb – by taking a sample of amniotic fluid (amniocentesis) – or after birth by taking a sample of the baby's blood
3)super-male:47,XYY syndrome is characterized by an extra copy of the Y chromosome in each of an individual's cells. Although many people with this condition are taller than average, the chromosomal change sometimes causes no unusual physical features.For some males with this syndrome, signs and symptoms are barely noticeable. For others, signs and symptoms may include learning disabilities, speech delay, low muscle tone (hypotonia), and being taller than expected.
4)super-female-Syndrome:It concerned a type of sex chromosome anomaly characterized by a chromosomal number of 47 and a chromosomal sex of XXX, and the authors used the term "super female" as a designation for this entity.
Symptoms associated with trisomy X include tall stature, mild developmental delay, subtle physical and skeletal anomalies, increased rates of mental health concerns, and earlier age of menopause.
These were explanations related to diseases caused by changes in the number of sex chromosomes that were presented to you.
In addition to diseases caused by changes in sex chromosomes, there are other diseases that occur due to changes in the number of somatic chromosomes (such as Down syndrome).
I hope you have used the above explanations.